Featured Projects

LLM Agents for System-Level Applications
Led the development of LLM agents to elevate user experience in system-level applications, including intelligent image editing in the Photos app and color recommendation features in digital painting tools for artists. Made use of multiple open source models like Qwen, Llava for different tasks.

Deep Research LLM Agent with Smart Editing
Designed a deep-research LLM agent leveraging Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) for comprehensive report creation, incorporating capabilities such as smart editing, multi-source content merging, and automated visualization. Made use of multiple open source models like Qwen reasoning, Mistral for different tasks.

LLM-Based Workflow Automation Agent
Built an LLM-based agent to automate user-recorded workflows in the Chrome browser, enabling cross-domain support for websites in entertainment, travel, food, and more, functionally similar to GPT-Operator. Made of use of multiple models for HTML data processing to identify the target element followed by action execution on that element.
Gesture Recognition with LLM Function Calling
Designed a gesture recognition ML model integrating LLM-based function calling to accurately interpret diverse hand-drawn and custom gestures made with a stylus on a tablet.

PEFT Model Fine-tuning for AI Applications
Fine-tuned large language models using Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) techniques like LoRA and adapter tuning to enable AI-powered sticker prompt generation in the Notes app and color palette creation in painting app. Finetuned LLama 3 model in pytorch with custom dataset and loss functions.

Advanced Computer Vision for Gaze Tracking
Led the research and deployment of advanced computer vision and deep learning methods for gaze tracking, achieving significant improvements in accuracy and performance for VR, desktop, and mobile applications. Worked on both RGB and IR cameras for gaze tracking.

SmartWatch based Heart Risk Monitoring System
Created end-end ML pipeline for monitoring heart health using smartwatch biomarker data.
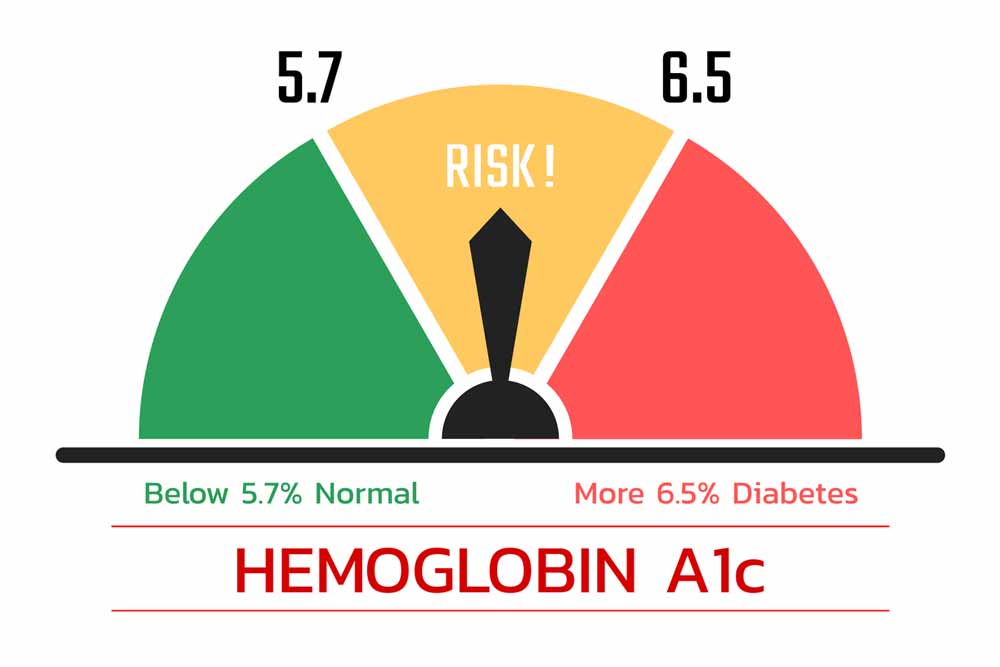
IoT-Enabled Smart Medical Devices
Developed robotic systems with IoT connectivity for measuring HbA1c levels in patients in a remote setting using finger-prick blood samples.